 |
 |
|
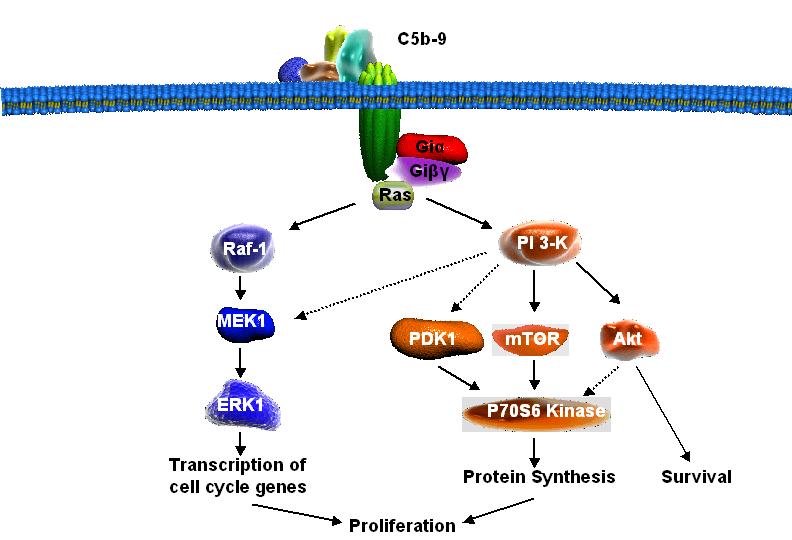
Signal transduction pathways activated by C5b-9 and required for cell proliferation(F. Niculescu, T. Ito 2007)
|
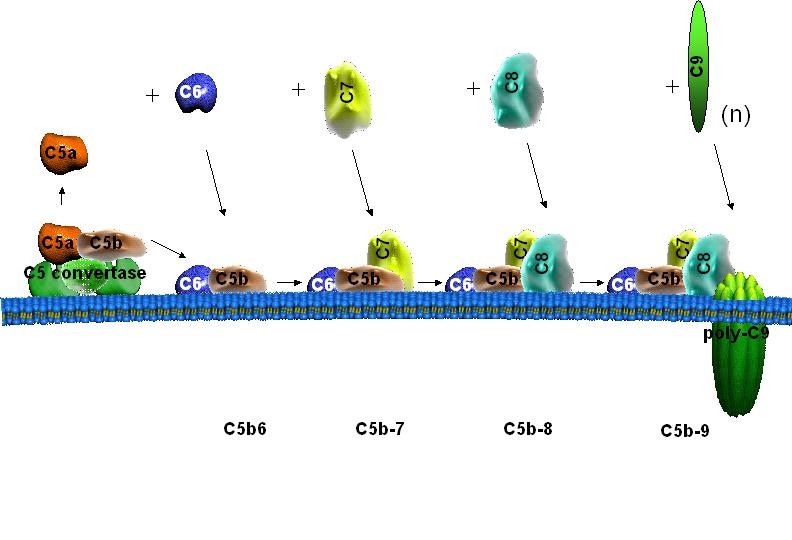
Figure 1 Assembly of terminal complement complexes C5b-7, C5b-8 and C5b-9. Activation of the C5 convertase occurs by the classical,alternative or mannose binding lectin pathways. C5 convertase binds and cleaves C5 into C5b and C5a. After binding to C5b, C6 acquires the ability to interact with the lipid bilayer and forms C5b6 bi-molecular complex. C7, then C8 sequentially bind to C5b and further insert into the lipid bilayer, forming C5b-7 and C5b-8 complexes, respectively. One molecule of C9 binds to membrane inserted C8, which is followed by polymerization of multiple C9 molecules forming C5b-9 complex.
|
|
|
 |
|
Figure 2 - Apoptosis of oligodendrocytes in culture. Rat neonatal OLG were culture in defined medium for 3 day and presence of apoptosis was tested by TUNEL
|
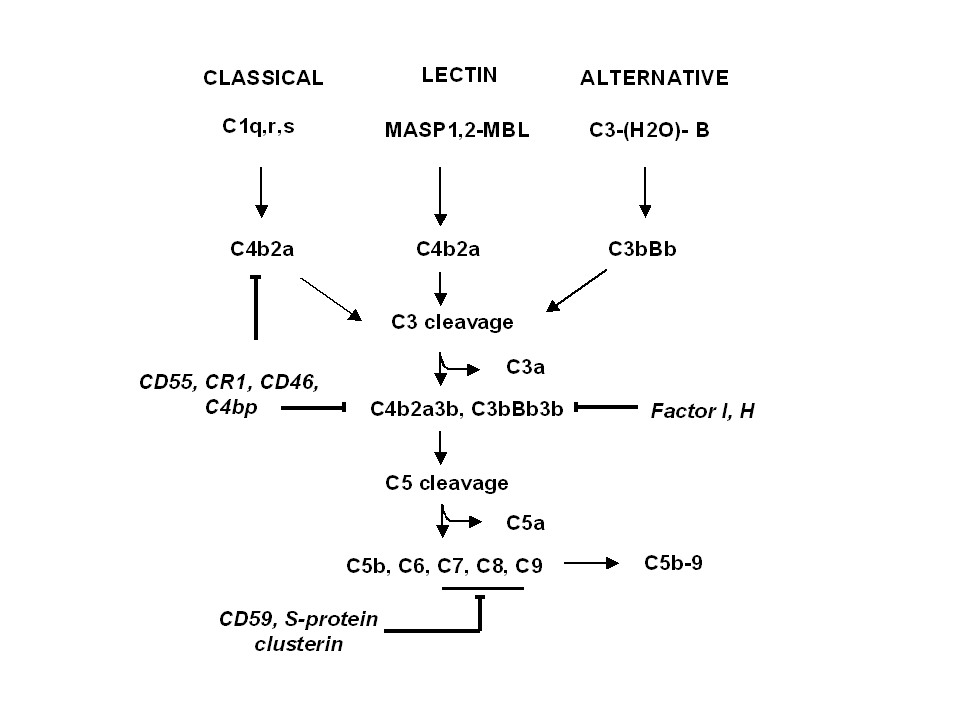
Activation of complement system and assembly of terminal pathway . Activation of classical, lectin and alternative pathways through specific activators leads to generation of C3 convertase (C4b2a and C3bBb) and C5 convertase (C4b2a3b or C4bBb3b). Generation of C5b allows activation and assembly of the terminal complement pathway leading to the formation of the C5b-9 complex. CD55, CR1, CD46, C4bp, and factors H and I regulates C3/C5 convertases. S-protein/vitronectin and clusterin are fluid phase inhibitors while membrane inhibitor CD59 down-regulate both the binding of C8/C9 to C5b-7 and the polymerization of C9. |
|
|
|
|
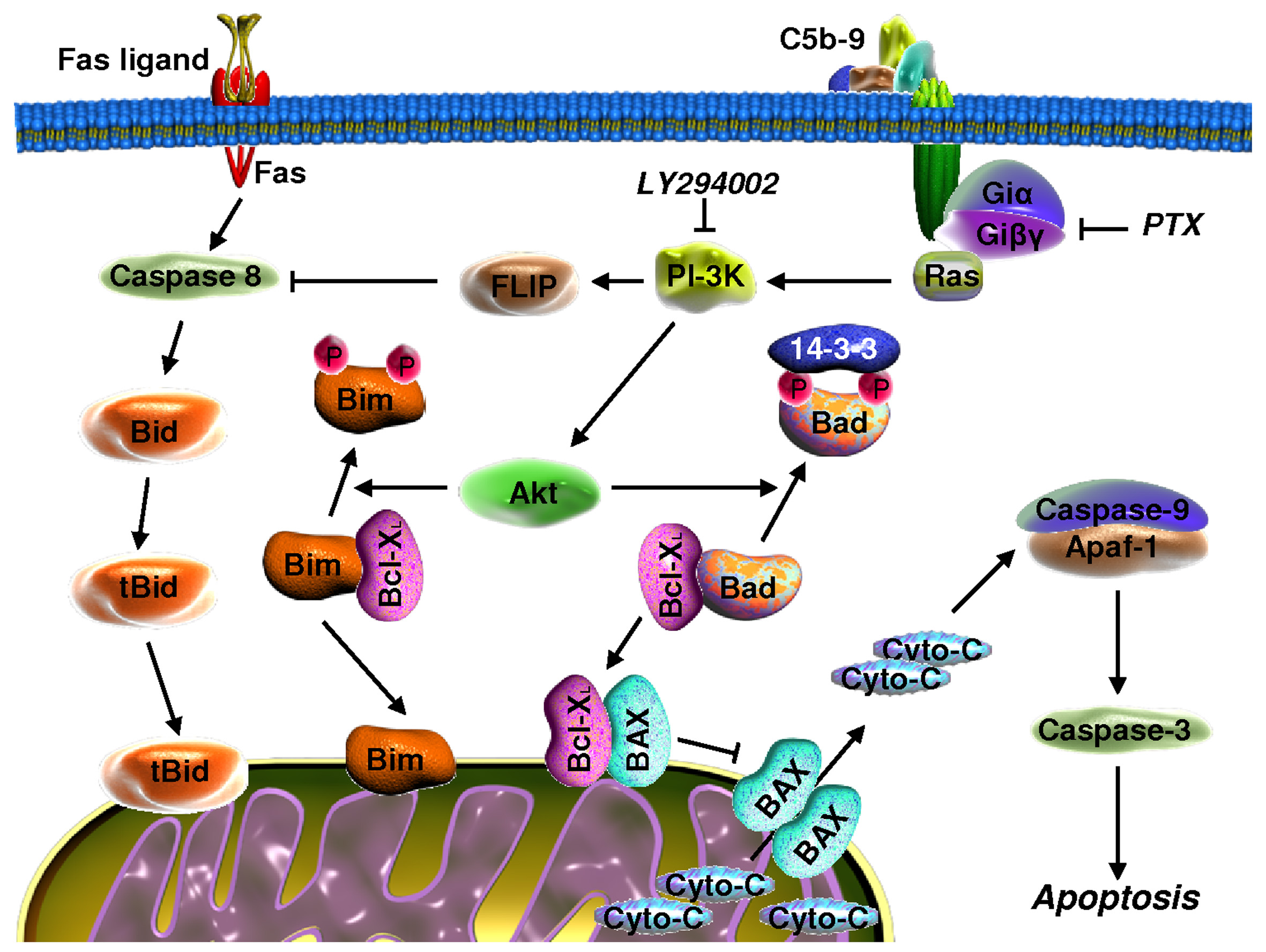
Signaling pathways that are activated by C5b-9 and involved in OLGs survival.
Insertion of the sublytic C5b-9 into the cell membrane leads to G-protein activation, followed by the activation of PI3K and Akt. Activation of PI3K induces up-regulation of FLIP and inhibition of caspase-8 processing, thereby inhibiting Fas-induced apoptosis in OLGs. Inhibition of caspase-8 processing is also responsible for the inhibition of Bid cleavage. Akt is able to induce the phosphorylation of Bad and Bim and protects the mitochondria from pore formation by Bax/Bak and cytochrome c release. All these signaling pathways result in the inhibition of apoptosis and OLGs survival. |
|
RusLab Home Page
subglobal1 link | subglobal1 link | subglobal1
link | subglobal1 link | subglobal1 link | subglobal1
link | subglobal1 link
subglobal2 link | subglobal2 link | subglobal2
link | subglobal2 link | subglobal2 link | subglobal2
link | subglobal2 link
subglobal3 link | subglobal3 link | subglobal3
link | subglobal3 link | subglobal3 link | subglobal3
link | subglobal3 link
subglobal4 link | subglobal4 link | subglobal4
link | subglobal4 link | subglobal4 link | subglobal4
link | subglobal4 link
subglobal5 link | subglobal5 link | subglobal5
link | subglobal5 link | subglobal5 link | subglobal5
link | subglobal5 link
subglobal6 link | subglobal6 link | subglobal6
link | subglobal6 link | subglobal6 link | subglobal6
link | subglobal6 link